What are the key principles of User Experience Design?
User experience design is a creative process that combines various disciplines to improve the user experience of a product or service. Its goals are to improve a product or service by adding value to the users’ experience. User experience design encompasses various design disciplines, including visual and information architecture. The following article discusses the key principles of user experience design. You’ll be better equipped to design for user needs than anyone else. To get started, begin by creating a persona, or character for your users.
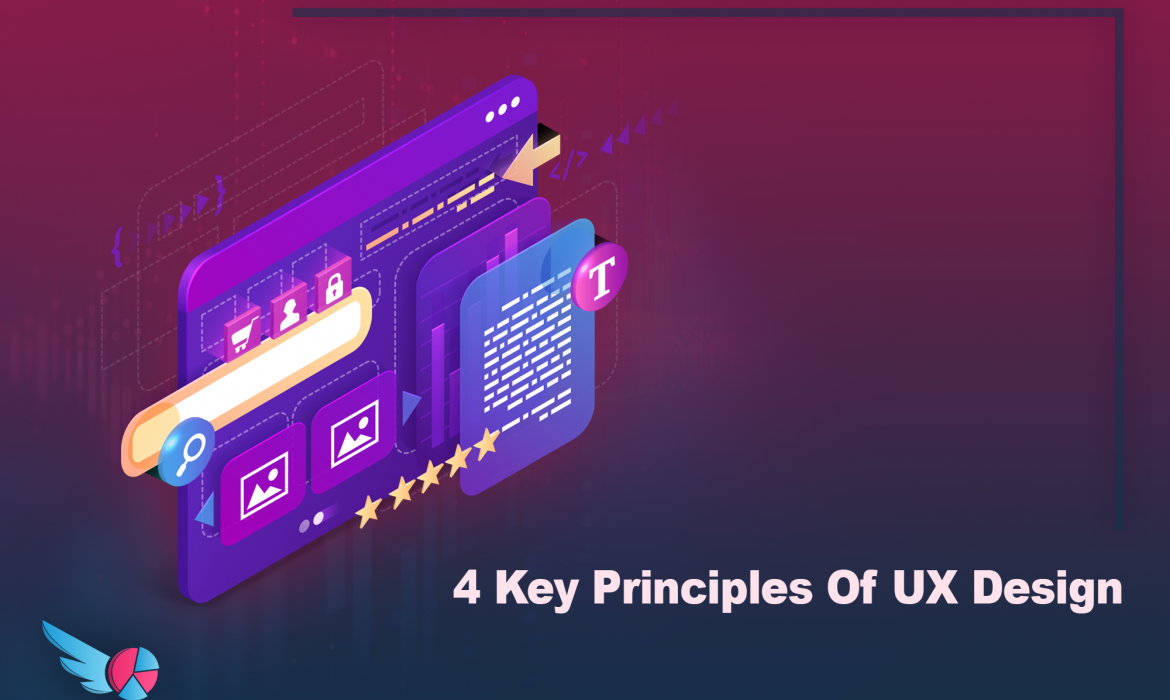
Human-centered design
Using human-centered design as a design approach is beneficial to UX designers as well as UI developers. The process of human centered design vs ux begins with a shift in mindset, whereby designers stop thinking about their users as “clicks” and instead think about their target users as “people.” Throughout the design process, they are encouraged to apply empathy and to reframe questions from the perspective of the final user. They should also consider the goals and needs of users, not just the wants and needs of their companies.
In order to make a successful product or service, the human-centered design must incorporate consumer testing into its development process. It is important to know the needs of your target market before beginning the design process. Using their feedback will help you refine your product and ensure that it will gain traction with the target audience. It is also important to keep in mind that human-centered design is cyclical. Sometimes, it is necessary to make changes as the product evolves to meet the needs of a wider consumer base.
We recognized consumer frustration and decided to create a solution. We embraced human centered design as a safer approach to solving problems. Ultimately, human-centered design makes for better user experiences and higher customer loyalty. When used correctly, the human-centered design will be beneficial for businesses in many ways, including long-term profitability and success. But there is a catch. It takes time.
The goal of human-centered design is to provide the best possible experience for your customers. For example, the creators of PayPal, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri all created a product that solves a customer problem. It’s also important to take into account how people use voice-assist technology. When customers use voice-assistant technology to find what they’re looking for, the human-centered design comes into play.
The human-centered design process is for anyone who wants to create a solution. It works well with any kind of product or service, and can be used in any phase of the design process. It’s a collaborative process that takes ideas from conception to completion. By focusing on the human perspective, designers can design products that satisfy people’s needs. And the results can be extremely satisfying. The process is an excellent choice for user-centered design.
Personas
A good way to begin using personas in your user experience design is to develop one for each of your main groups of users. These personas are often classified by age, technical ability, and motivations. The primary persona is the type of user who interacts with your product, and the secondary persona is the one who makes decisions about the product. This is often the most common type of user, and should be considered when designing your next website or application.
In order to create a good user experience, it’s essential to identify your target audience. Without knowing who your target audience is, you may end up designing for yourself. By creating a persona, you’ll have a better idea of the type of product or service your audience wants. Besides, you’ll be able to see what works best for the target audience and how they spend their time. This information will help you create a more effective product and service.
Creating personas is crucial if you want to create a successful product. By developing a realistic representation of real users, you can make informed design decisions and gauge the efficacy of your designs. Using personas can also help you develop empathy and connect with your customers. The process of creating personas is an iterative process, so make sure to make use of the best tool for the job.
Using personas in your user experience design is a great way to avoid self-referential thinking and create a better product. Instead of working from an idealized picture of a potential customer, you’ll be designing for real people with their needs, motivations, emotions, and frustrations. Personas also help you build consensus among your team members, exposing any areas of disagreement and ensuring everyone on your team is on the same page.
Usability
In general, usability refers to the ease with which a person can complete a task. Usability also includes the information architecture and user interface. For example, a poorly designed website can make searching and browsing more difficult. Likewise, poor user experience can reduce the chances of a customer converting to a paying customer. In general, usability refers to a site’s usability, so it is important to ensure that your site meets the expectations of users and is usable and easy to use.
A usability strategy begins with goals and then includes methods for improving ease of use. For example, an internal team may analyze calls to action to make the site easier to navigate. A usability strategy is an important part of a user experience design because it helps the internal team learn about the user and how they want to be treated. Good usability is one of the best ways to gain the trust of users, and a poor user experience can damage a company’s reputation and the bottom line.
In terms of user experience design, usability measures the effectiveness, satisfaction, and ease of use of a product. While UI design is an important component, usability also considers the technical aspects of a system. During testing, users perform various tasks to assess how easy or difficult it is to operate a product. Usability is a key factor in creating an app or website, as users are able to learn new tasks quickly and easily.
In the case of website usability, the goal of UI is to get the user from point A to point B. It must help the user achieve their goals, as well as business goals. It should also provide clear signals for next steps, success, and confirmation. These signals encourage engagement and conversion. By ensuring usability, websites or apps are both functional and usable, and ultimately successful. A website that is not usable, despite having all the necessary features, is a complete waste of time and energy.
While usability is essential in product usability, accessibility is also important in ensuring that all users can access products and services. In particular, accessibility refers to the process of making products usable for people with disabilities. In addition to ensuring accessibility, usability also measures a product’s ease of use. In other words, accessibility is about making products more enjoyable for people of all abilities. In this way, usability is important in ensuring that a product is usable for everyone.
Testing
A thorough testing plan is crucial to ensure your UX is optimized for your target audience. It lays out the purpose of the test, the methodologies to be used, and the users and scenarios that you will be testing. Your plan should also include learnings from the research and what to do next. By following a plan, you can avoid making costly mistakes and make sure your testing is focused on the right goals. Below are some tips for testing your UX.
Prototypes can be a great way to test UX elements and identify user patterns. Prototypes are a great way to collect data and make changes before the final design is ready. This approach can save your company time, resources, and money while getting a better understanding of your users. This will also help you make more informed design decisions. In addition, prototyping your UX will help you learn about your users’ needs and preferences and can lead to a better product.
The most popular technique is the card sorting method. This method helps you prioritize content in your user interface. Essentially, you place concepts on cards and let participants manipulate and explain the meaning of each card. After the test participants have completed the tasks, you’ll be able to get a better understanding of how your UX can impact their overall experience. If you want to create a successful user experience, use these methods to test your UX design and make sure it’s optimized for your users.
First, you’ll need to identify the end-user. You need to have an idea of what the end-user will need and find candidates who have the right skill sets. Without knowing this, you could risk invalidating your results. Next, transform your solution into an interactive prototype. You can then present the prototype to test subjects during the test. But be sure not to use high-fidelity prototypes as they may be confused with a live product.
The benefits of UX testing go far beyond reducing project costs. They increase the chances of a successful product while reducing unnecessary development efforts and reducing the likelihood of failure. Whether you’re designing a product for a large company or a small startup, UX testing can help you understand what makes your customers tick. You can also use the results of testing to make improvements to enterprise and B2B business models. By incorporating these techniques into your UX design, you’ll be more confident about what your target audience likes and needs.
The 4 Key principles of user experience design
The Product Design UX Process
If you want to understand the product design ux process, here are some basic steps that you should take before you start working on your product. You should define the type of product you’re designing, who your target audience is, and any problems they may encounter. Your design should also address the context and environment in which your users will use it. Hopefully, this information will help you to create a better product and make your customers happy!
Often, entrepreneurs believe that their products will meet the needs of users without analyzing their needs. This often leads them to misinterpret and belittle the implications of user needs, thereby missing an opportunity to maximize the benefits of the product. It is critical that product designers conduct research, especially when they are developing a product for a business that has limited or no business plan. Even if you’re only starting out, conducting competitive audits can help you understand your customers and what they need.
The product design ux process should begin with user research and user testing. The goal of this phase is to gather insights about user needs, wants, and expectations, which will help them develop the best product possible. This phase is highly iterative and requires active participation from all team members. Moreover, it’s crucial to understand what the stakeholders are really looking for. If your product doesn’t meet the expectations of users, you’re not designing a successful product.
Product design, UX, UI, What is the difference between them?
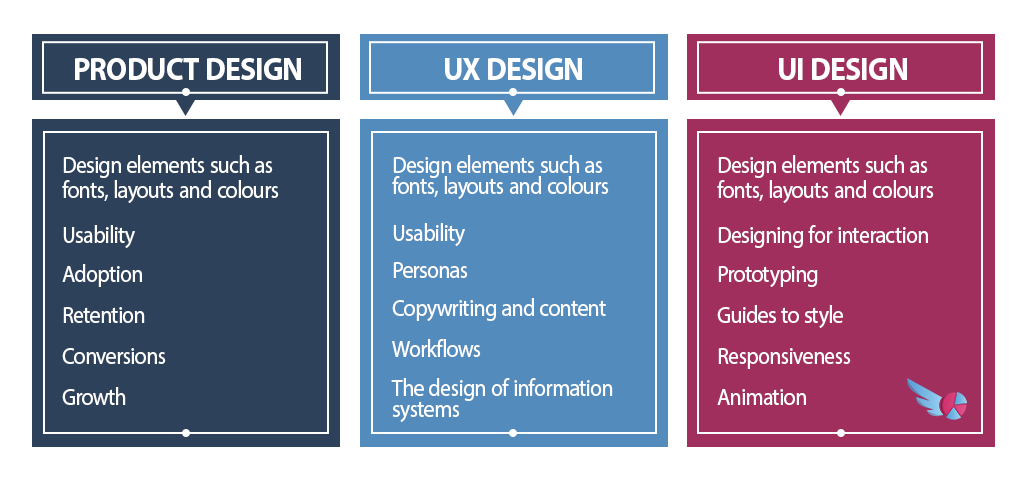
Product design vs. UX design vs. UI design
Product design:
The goal of product design to create a product that fits the needs of both the customer and the company. They ensure that the business’s challenges are turned into great experiences for the customers who also have a problem to be solved. Designers in this field have a comprehensive awareness of the product’s target audience and the company’s goals, as well as a profound understanding of how to best meet those goals. Product Designers can handle the business’s particular goals of adoption, conversion, retention, and growth by utilising design.
Product designer:
Product designers are in charge of every step of the product development process, from brainstorming through manufacturing. As soon as they identify a gap in market demand, they transmit the problem of real users to experts in the field, and they come up with an appropriate solution. To put it another way, a product designer’s job is to strike a balance between corporate objectives and the wants and needs of end customers.
The UI design:
The design of the user interface. When it comes to product design, UI Design or user interface design is the most important aspect. UI Designers strive to create a cohesive, enjoyable product that includes animations, responsiveness, and a consistent style guide for the product to follow. However, the product’s usefulness is where UI design falls short. Despite its appealing appearance, the product’s user experience falls short: perhaps it’s tough to browse or the information hierarchy isn’t clear, making it difficult to find what you’re searching for or making it difficult to complete your work. Designers of user interfaces treat their work as an art form, however, they are sometimes unable to translate the aesthetics of their work into a functional result.
User Interface (UI) Designer:
UI designers are in charge of creating a user interface, which must be both simple to use and stand out from the crowd. It is not a simple effort to make a product user-friendly. In order for a functional interface to be visually appealing, it must also be functional. People’s eagerness to interact with any product is heavily influenced by its user interface.
User Experience design:
As a result of the disparity between the product’s appearance and its experience, UX design was born. User needs, wants, and goals are the primary emphasis of UX designers. When it comes to user experience (UX) design, iteration and research are a constant part of the process. To comprehend the user’s overall workflow, they also take a look at their product’s place in it.
Despite the fact that UX design is still an essential and renowned field, the increased focus on the user has shown a significant flaw in the discipline. The UX designer has the ability to build a product that both delights the user and provides a positive user experience.
User Experience (UX) Designers:
The UX professional should ensure that the user has an enjoyable experience. When a product has an intuitive design, which implies making it easy for the target audience to utilise, you can establish long-term interaction. As a result, a UX designer should be able to foresee all possible user journeys and identify any obstacles they might encounter.
UI vs UX:
With the help of prototypes and user research, one may forecast numerous scenarios for the UI. Only one side of the coin can be considered. User experience (UX) refers to the product’s visual depiction. The user experience can be improved by ensuring that all aspects (colours, fonts, etc.) are aligned with the user’s wants, business goals, and customer expectations.